This is an update on the ADS-B device. I have written about this in the previous two communications, here and here. So, on Tuesday 2nd August the Raspberry Pi arrived. Since then I have been setting it all up so the receiver is no longer dependent on the PC being on.
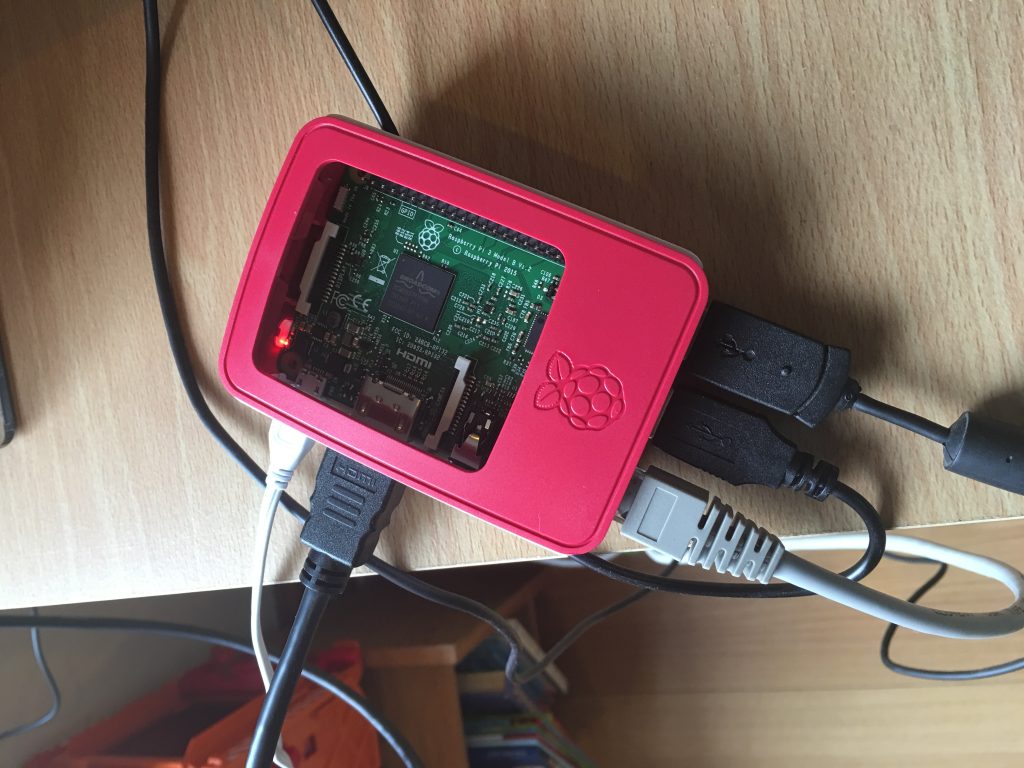

The first thing was to install the correct OS on the Pi. The picture shows it in initial phase with monitor, ethernet, keyboard and mouse all connected. Once the OS was installed I had to tell it to not load the GUI and just run a command line. Then, I got it connected to the network and pretty much removed all the cables apart from power.
I can connect to the Pi using SSH and run script from the command line. Next phase was to load the USB stick drivers and software. This was reasonable. Next up was the ADS-B reading software, installing and getting it running seemed easy enough and then I had to adjust some code to make sure this service starts up from boot. Next software to load was the MLAT server program, this was easy enough although initially I couldn’t quite find the correct code to check it was running.
Then, the whole set up was tested in the dining room window.

Today has been the task of moving the unit to the loft. I didn’t have any power sockets up there so one had to be installed and that took the time! Once that was done the system just needed to be secured onto the main beam in the loft. The important thing is to keep the length of the cable from aerial to dongle as short as possible, this increases the signal going into the Pi. The loft set up has been tested and it is running fine.

I have access to the Pi either via the PC using a program called PuTTY or the iPhone using an SSH connection. I can shut down the Pi remotely and monitor the internal temperature of the device. It is running at a range of 50-60 Celsius. Using a Pi to run this software is a bit like taking a sledgehammer to a walnut. But, it is independent and runs remotely. I am happy this procedure was reasonably straight forward!
The next stage is to get a more specialist aerial and maybe a more specific USB Dongle. However, this is one of those things where the amount of money you spend can be unlimited. You know, I could just install a radar up in the loft. However, here is the current splat for the range of the aircraft from my ADS-B receiver.
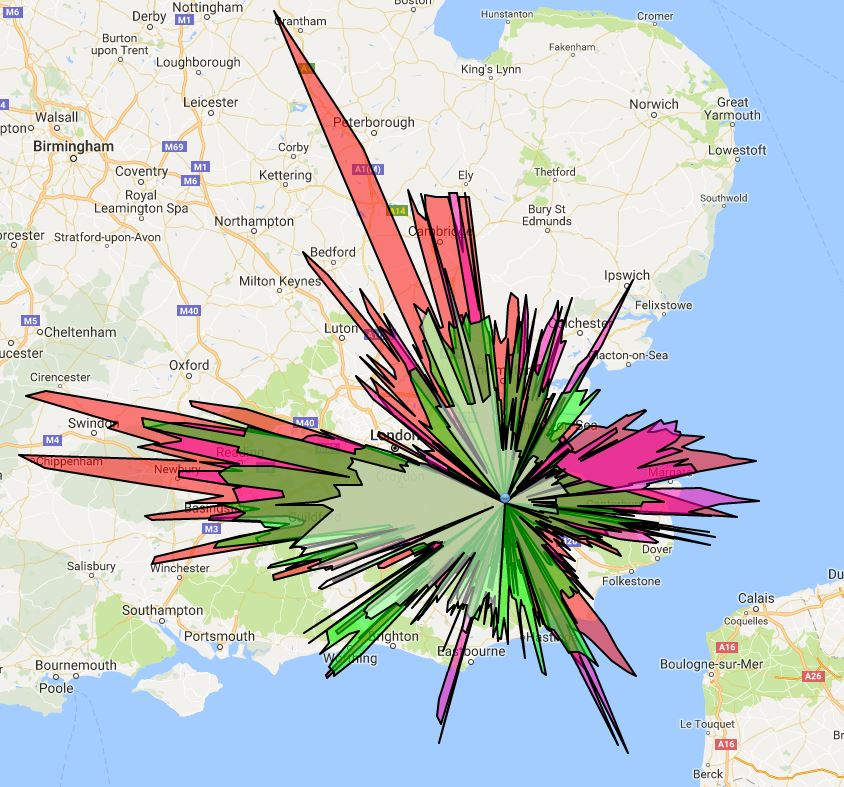
Now that I’ve been reading a bit more about this type of thing I can explain a little more. ADS-B is broadcast by many aircraft and they send this on 1090MHz. These are the signals I receive in the loft and can see on my Virtual Radar Server software. I also send these signals over the internet to a new “radar” website. The ADS-B signals contain bits of information about position and heading, these are sent to a server which can determine positions of other aircraft by using time differences between signals arriving, this is called MultiLateration or MLAT. My Pi is part of this network allowing Radar360 to “see” more aircraft than just ADS-B alone.
