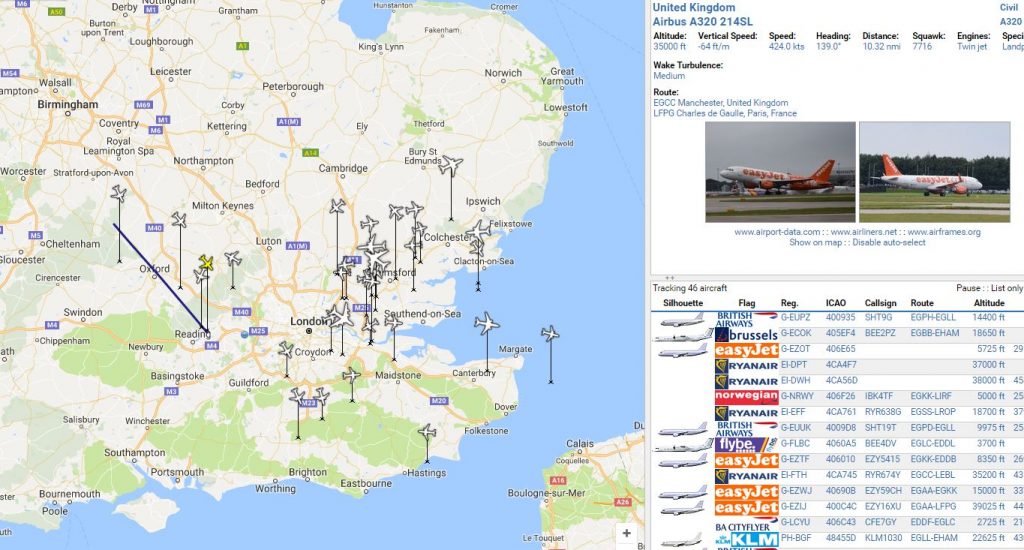
These communications contain many items concerning the virtual radar system that lives in my loft and you can see a selection here. A short while ago I decided to buy an pre-amp and filter for my system to improve the range and number of aircraft being received. So, this communication now requires a large number of pictures to give you an idea of what this means.
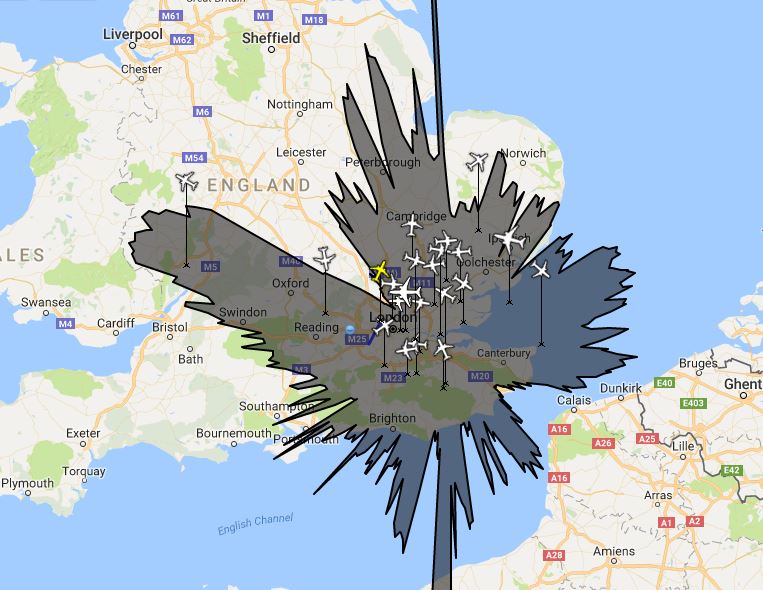
In the above picture you can see that there are around 20 aircraft and the black area [the range of the receiver] doesn’t quite reach Norwich, Portsmouth, Bristol or Calais. There is the NW-SE block as described before.
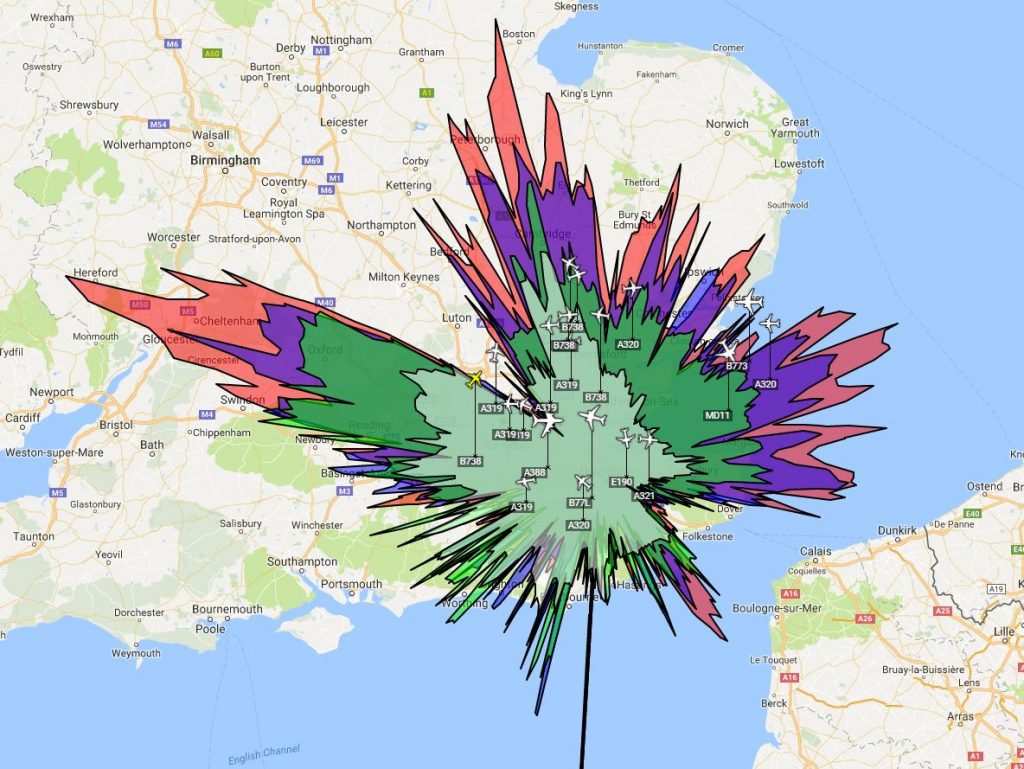
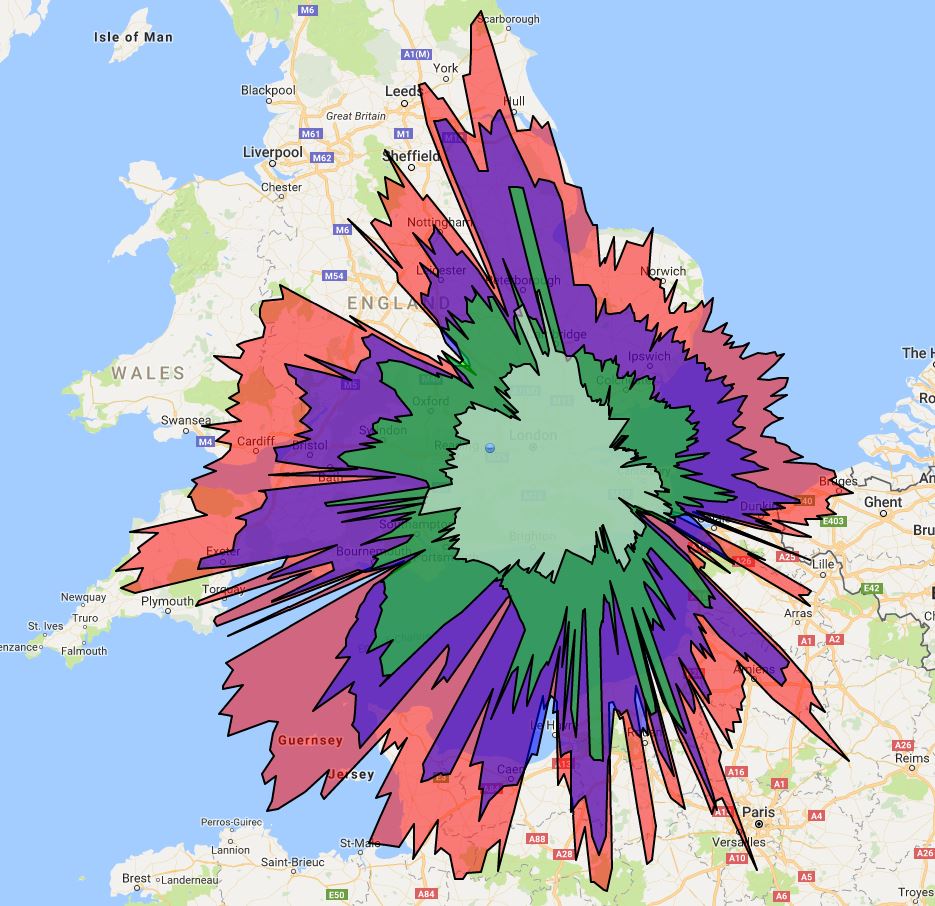
This coloured splat gives pretty much the same information but uses colours for the ranges of aircraft at different altitudes.
I bought a filter which only allows signals close to the 1090MHz requirement through to the USB stick I bought. It also acts as a pre-amp so there is an overall 14 dB gain.
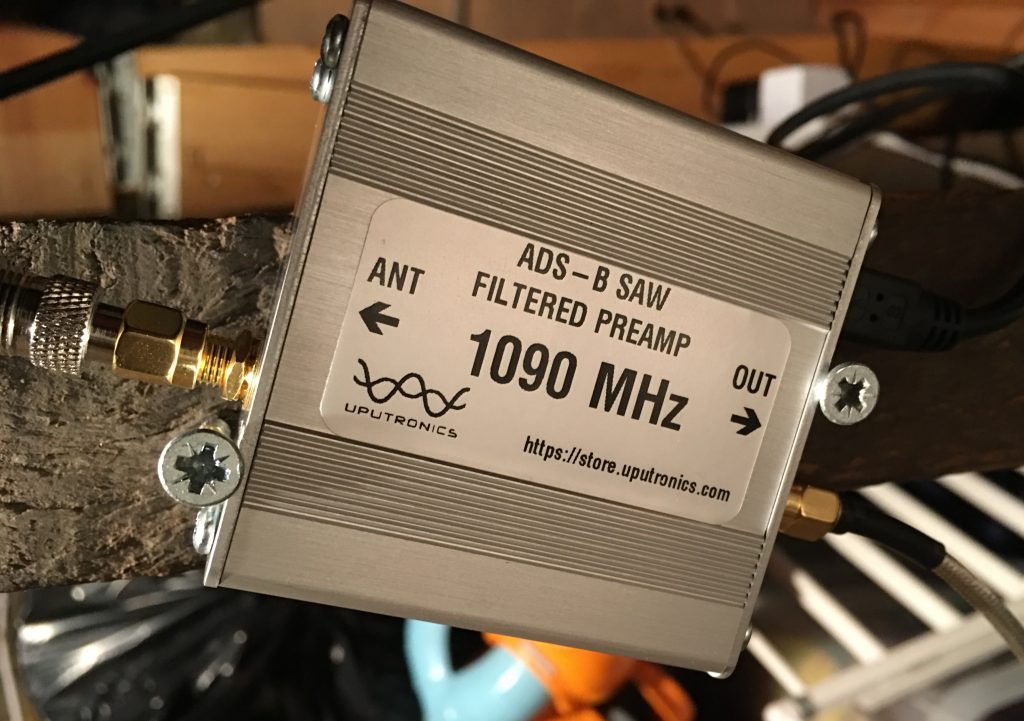
Here is the whole Virtual Radar system living in the loft:

Once this kit was turned on I looked at the DUMP1090 output from the Raspberry Pi and pretty much shat myself at the number of aricraft shown:
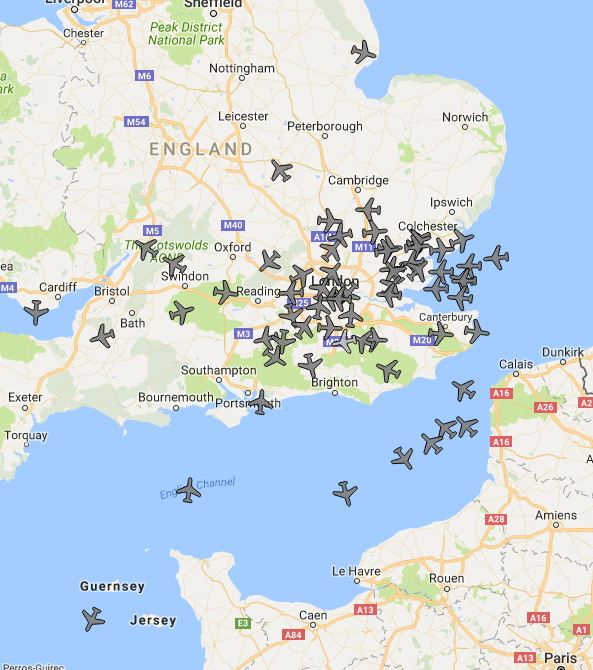
When this view is compared to the twenty or so aircraft that I had before you can see an immense improvement in the receivers ability.
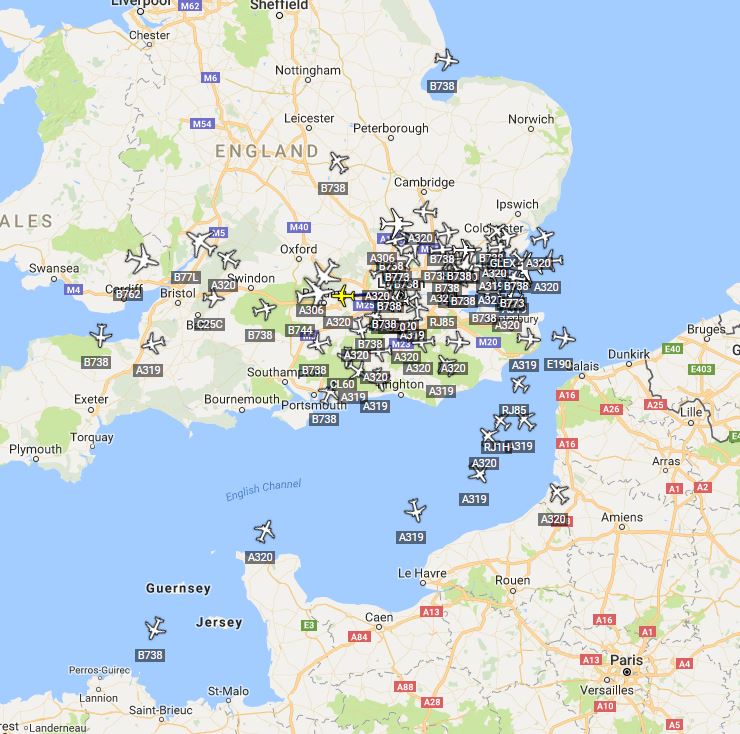
Virtual Radar Server is a program I use on the RPi for a more detailed view, there are quite a few customisations you can create also. It is the software that will create the splat over time, keeping track of the aircraft and their position.
The distances have increased as has the overall coverage. I now track around 100 aircraft at a time. For a small sum of money the overall increase in detail has been terrific. I can now reach over northern France, over Wales and a lot of the channel to the SW.
A side by side comparison.